JetRacer: Spurführung mit künstlicher Intelligenz

Autor: Evrard Leuteu
Art: Projektarbeit
Starttermin: TBD
Abgabetermin: TBD
Betreuer: Prof. Schneider
Einführung
Installation der virtuellen Maschine VirtualBox
Aufgabenstellung
- Einarbeitung in das bestehende Framwework
- Optimierung der KI für den Rundkurs im Labor Autonome Systeme (Geschwindigkeit, Robustheit).
- Optimierung des Reglers (z. B. PD-Regler)
- Nutzung von MATLAB zum Anlernen des Jetson Nano.
- Drive the JetRacer in the right lane counterclockwise with the gamepad controller. Limit the speed via Software to a maximum (e. g. 1 m/s).
- Take a video while driving a lap with MATLAB® using a MATLAB®-script.
- Load the pretrained NN.
- Train the pretrained NN with MATLAB® with a MATLAB®-App (GUI) by clicking the desired path in the images.
- Option: Use classic lane tracking algorithms to teach the NN automatically.
- Write a PD-contoller that uses the NN to drive in the right lane. Program this in MATLAB® and let it run on the JetRacer-GPU using GPU Coder.
- Goal: the car should drive autonomously several laps in the right lane as fast as possible.
- Dokumentation nach wissenschaftlichem Stand im HSHL-Wiki
Anforderungen
Das Projekt erfordert Vorwissen in den nachfolgenden Themengebieten. Sollten Sie die Anforderungen nicht erfüllen müssen Sie sich diese Kenntnisse anhand im Rahmen der Arbeit anhand von Literatur/Online-Kursen selbst aneignen.
- Erfahrungen mit Künstlicher Intelligenz/Deep Learning
- Programmierung in C++, Python
- Dokumentenversionierung mit SVN
Anforderungen an die wissenschaftliche Arbeit
- Wissenschaftliche Vorgehensweise (Projektplan, etc.), nützlicher Artikel: Gantt Diagramm erstellen
- Wöchentlicher Fortschrittsberichte (informativ), aktualisieren Sie das Besprechungsprotokoll - Live Gespräch mit Prof. Schneider
- Projektvorstellung im Wiki
- Tägliche Sicherung der Arbeitsergebnisse in SVN
- Tägliche Dokumentation der geleisteten Arbeitsstunden
- Studentische Arbeiten bei Prof. Schneider
- Anforderungen an eine wissenschaftlich Arbeit
Projektplan
SVN-Repositorium
Getting started
Lesen Sie zum Einstieg diese Artikel
- Siddiquy, T.: Automated lane following of a Waveshare JetRacer with artificial intelligence. Bachelorarbeit
- Kamal, A.: JetRacer: Optimierung der Streckenführung. Projektarbeit
- Gantt Diagramm erstellen
- Tipps zum Schreiben eines Wiki-Artikels
- PAP Designer Einstieg
- Einführung in SVN
Understand the existing system framework
Optimize AI for speed and robustness in the lab
Improve the controller (e.g., PD controller)
Use MATLAB to train on Jetson Nano
Drive JetRacer counterclockwise using a gamepad, limiting speed (e.g., 1 m/s)
Record a lap using a MATLAB script
Load and retrain a pretrained NN with a MATLAB GUI
Optionally, automate NN training with classic lane tracking
Develop a PD controller using the NN, coded in MATLAB for JetRacer GPU
Summary
- Firstly connecting to the Jetracer and MATLAB according to the [1] MATLAB documentation, which help up to setup the full process.
- For modeling the project it can be make as simple as possible to understand the steps to follow, in this paper [2],it shows some of the ideas and implementation can be done.
- A outline of the line following algorithm diagram can be:

- Firstly the camera configuration, Detecting the Jetracer camera then creating a video input object to set all the parameter like frame rate, resolution and others. Then the image acquisition can start its video labeling. [3]
- For image acquisition after setting up camera, it start capturing image on fixed parameter which has been set. Image Processing for the line following starts as a capture the lane data from track, then convert it to grayscale image. Also applying edge detection(Canny), thresholding to locate the line and process the data. Then it continues the loop for the full process.
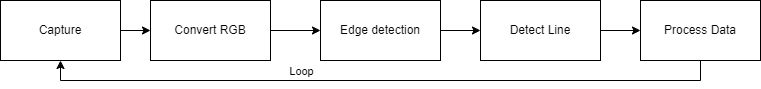
- After getting all the data its time for analyze and make it setup for the Jetracer. While from the frame capture extracting the following line feature is main goal. Line positioning, direction of car, prediction of the path to follow next is also part of the process. All the analysis process the speed and steering control gets calculated to create a PID controller.
- Controlling the Jetracer with PID controller has various complex steps to follow such as maintaining the speed, line, steering angle. Setting up the PID values to minimum at first then after identifying the error rate of the predicted line. Then tuning the parameters of the PID help to get the control results.
- The structure of the model is divided in various part:
main.m: Contains the main loop and integrates other modules. camera.m: Contains code for camera initialization. processimage.m: Handles image processing & find line to follow. PID_controller.m: Manages the PID control logic. adjustSteering.m: Contains the code to adjust the Jetracer's steering.
Mögliche Folgethemen
- Kreuzungserkennung
- Vorfahrterkennung
- Hinderniserkennung und Umfahrung
- Schildererkennung
Nützliche Artikel
- Deep Learning with MATLAB, NVIDIA Jetson, and ROS
- NVidia: JetRacer
- formulaedge.org
- Waveshare Wiki
- FAQ: Matlab to control jetracer(jetson nano tx1) motor
- Towards Autonomous Driving with Small-Scale Cars: A Survey of Recent Development
- Lane Detection in ROS 2 Using Deep Learning with MATLAB
- Train DQN Agent for Lane Keeping Assist
- Build Neural Networks for Self-Driving Cars with MATLAB
- DLI Training: Deep Learning for Autonomous Vehicles
- Machine Learning with Simulink and NVIDIA Jetson
- Comparative Transfer Learning Models for End-to-End Self-Driving Car
- Multi-task deep learning with optical flow features for self-driving cars
- Train DQN Agent for Lane Keeping Assist
- Real-Time End-to-End Self-Driving Car Navigation
- Hello AI World
- Jetson AI Courses and Certifications
- NVIDIA Developer Forums
- ChatGPT Anleitung für einen Lane Following Algorithmus
Literatur
Schreiber, C.: KI-gestützte „Follow-Me“-Funktion am Beispiel des JetRacer. Mittweida, Hochschule Mittweida – University of Applied Sciences, Fakultät Ingenieurwissenschaften, Masterarbeit, 2023. URL: [4]
→ zurück zum Hauptartikel: Studentische Arbeiten