Robot Operating System: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
| Zeile 36: | Zeile 36: | ||
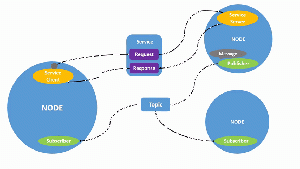
== Terminologies in ROS == | == Terminologies in ROS == | ||
[[Datei:Nodes-TopicandService.gif|left|mini|300px|Abb.1 <nowiki></nowiki>]] | |||
<br clear = all> | |||
Version vom 15. März 2022, 20:16 Uhr
Autoren: Fawad Murad
Betreuer: Prof. Schneider
Art: Praxissemester
Projektlaufzeit: 02.11.2021-20.02.2022
What is ROS?
ROS stands for Robot Operating System and it is an open-source platform that makes it easier for researchers and developers to create and reuse code for robotics applications. ROS is also a global open-source community of engineers, developers, and enthusiasts that work to improve, expand, and make robots more accessible to the general public. ROS is not an actual operating system but it is more like an environment. The big strength of ROS is its ability of connecting nodes together.
Why should we use ROS for robotics?
Due to the following reasons, one can analyze the advantages of using ROS for robotics:
Language-agnostic
A Python node and a C++ node can readily communicate with each other. It implies a lot of reusability and coworking possibilities. Because ROS is primarily focused on C++ and Python, several modules also allow you to use other languages. We can also install a websocket server (rosbridge suite) or an HTTP server on our robot and communicate with it using any language.
Light
ROS's core doesn't take up a lot of space or resources. In only a few minutes, we can install the essential packages and get started. Furthermore, ROS may be used on embedded computers like Raspberry Pi 3 boards. As a result, we may immediately begin a new project with minimal effort.
Packages for everything
Do you need to calculate a robot's trajectory? That is anything for which there is a package. Control the robot using your joystick? There is a package for that as well. Or perhaps you want to use a drone to map out a room? There are numerous software available to accomplish this. If you do a little searching, you'll find a plethora of ROS packages for practically every robotic application.
Great simulation tools
We require simulation tools since we cannot always get our robot to run in real time. Webots, Rviz, and Gazebo are just a few of the fantastic tools available in ROS. For educational purposes or to test in a specific context, the simulation tools can allow us to observe and utilise other robots that we do not own.
Control multiple robots
Multiple ROS masters can be used with ROS. It means that we can have a large number of autonomous robots, each with its own ROS system, and they can all communicate with one another.
Terminologies in ROS