Jetracer Kamera
Kamera Node einschalten
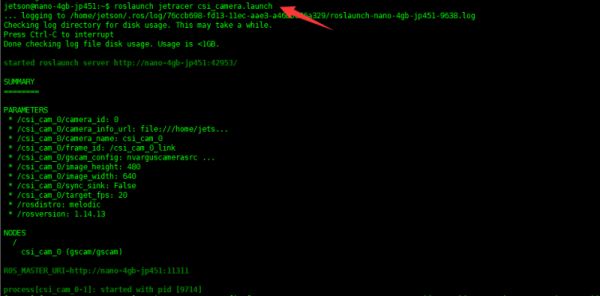
- Öffnen sie ein Terminal auf dem Roboter und geben sie folgenden Befehl ein, um den CSI Kamera Knoten zu starten.
roslaunch jetracer csi_camera.launch
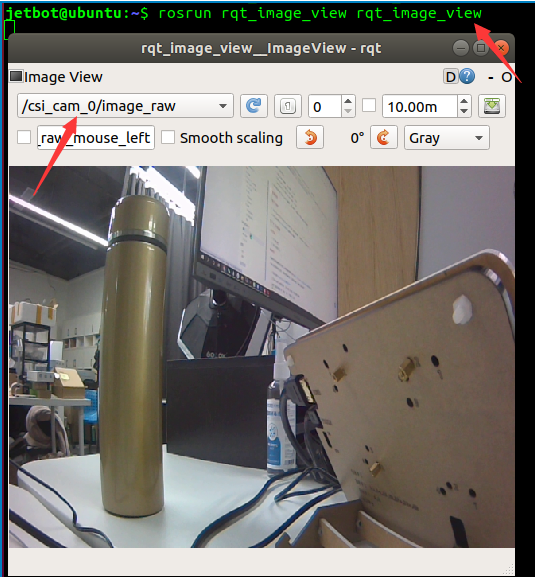
- Sobald der Kamera Knoten gestartet ist, können sie in der Virtuellen Maschine durch folgenden Befehl das "Image Viewing Interface" öffnen.
rosrun rqt_image_view rqt_image_view
- Es kann zwischen zwei Moden ausgewählt werden, /csi_cam_0/image_raw und /csi_cam_0/image_raw/compressed. Sie stehen jeewils für rohe Daten und komprimierte Daten. Es ist besser den komprimierten Modus zu wählen, da dieser die benötigte Bandbreite reduziert.
Video in RVIZ anschauen
- Öffnen Sie erneut ein Terminal in der virtuellen Maschine und führen Sie den Befehl rosrun rviz rviz oder rviz aus, um das RVIZ Programm zu starten.
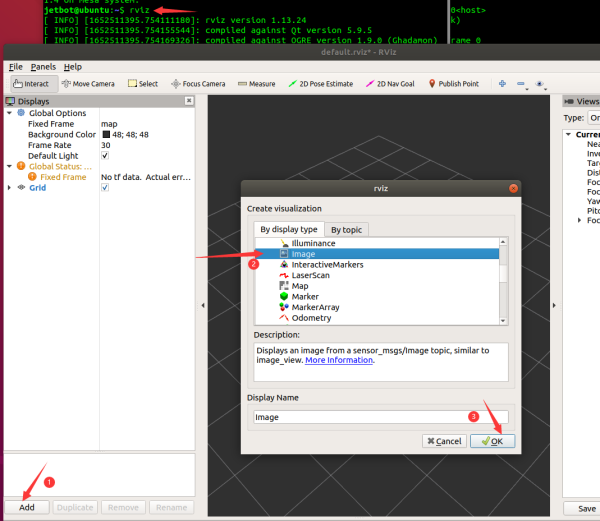 Fügen Sie die Bild-Komponente hinzu, wählen Sie das entsprechende Thema /csi_cam_0/image_raw und wählen Sie die komprimierten Daten als Übertragungsart, um das Bild anzuzeigen.
Fügen Sie die Bild-Komponente hinzu, wählen Sie das entsprechende Thema /csi_cam_0/image_raw und wählen Sie die komprimierten Daten als Übertragungsart, um das Bild anzuzeigen.
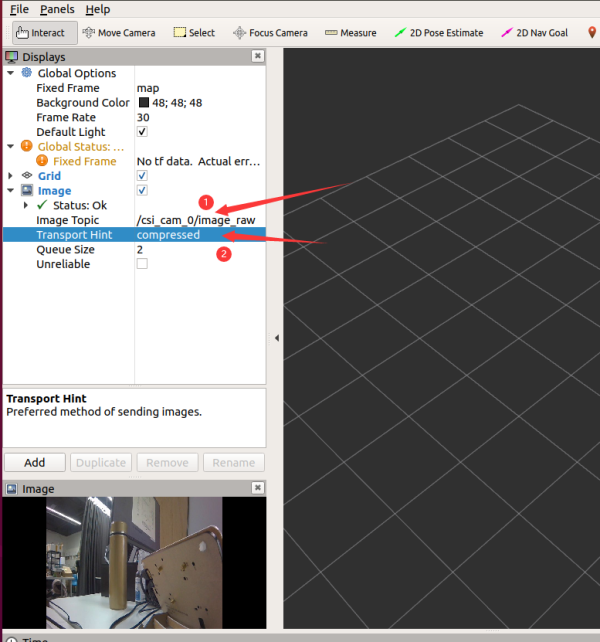
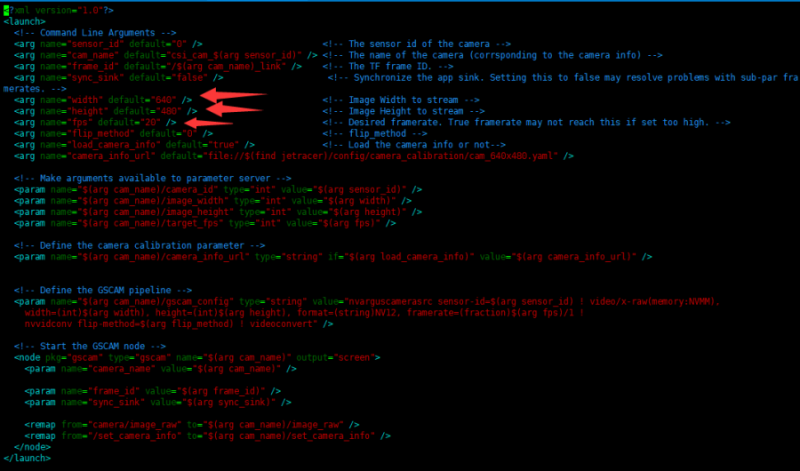
- Sie können die Auflösung und die Bildrate ändern, indem Sie die Startdatei jetbot_pro/launch/csi_camera.launch ändern. Beachten Sie, dass je höher die Auflösung, desto höher die Bildrate, desto größer die benötigte Bandbreite und desto leichter kann das Bild einfrieren.
- Geben Sie den folgenden Befehl im Terminal auf dem jetson nano ein, um die Auflösung und die Bildrate zu ändern.
sudo nano catkin_ws/src/jetbot_pro/launch/csi_camera.launch
Kamera kalibrieren
- Geben sie den folgenden Befehl auf Seiten der virtuellen Maschine ein, um das Kalibrations Interface zu öffnen.
rosrun camera_calibration cameracalibrator.py --size 5x7 --square 0.03 image:=/csi_cam_0/image_raw camera:=/csi_cam_0
- Hierbei stehen die Variablen für:
- size: Die Anzahl der Schwarzen und Weißen Kanten auf dem Brett, hier wäre es also ein 5x7 kariertes Brett.
- square: Die Seitenlänge des Schachbretts in Metern.
- image and camera: Der Modus in dem die Bilder gesendet werden.
- Hier kann auch das Schachbrett welches im Labor ist benutzt werden, dann müssen aber die size und square Werte im Befehl entsprechen angepasst werden.
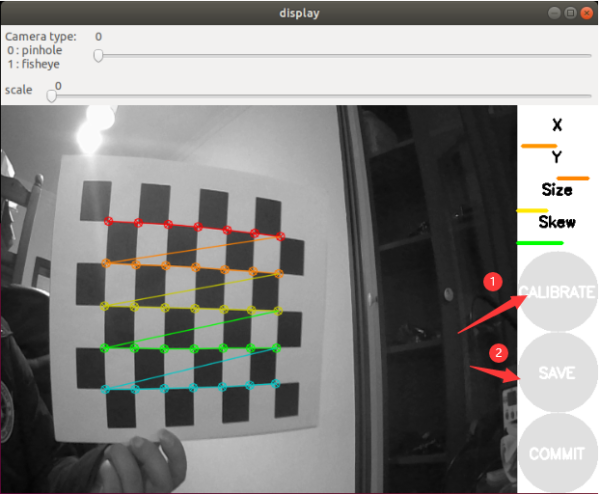
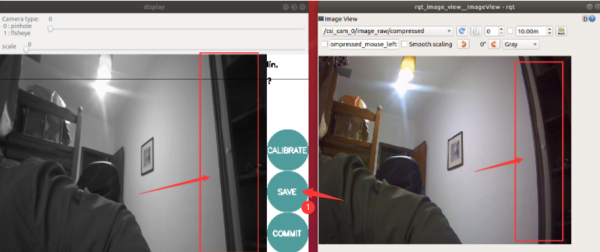
- In order to obtain better calibration results, it is necessary to move the checkerboard to different positions of the image, especially the edge positions of the image. When the CALIBRATE button changes from gray to green, it means that enough data has been collected, you can click CALIBRATE to view the results.
- Click the "CALIBRATE" button, the calibration program automatically calculates the calibration parameters, it takes a while, the interface may become gray and unresponsive, be careful not to close it and wait for a while.
- After the calibration is completed, you can see the calibrated image through the graphical interface. By comparison, you can find that there is a deformation on the right side until a good calibration effect is obtained.
- Click "SAVE" to save the calibration data to the temporary file of the virtual machine, click "COMMIT" to save the calibration file to the robot configuration file, the default directory is
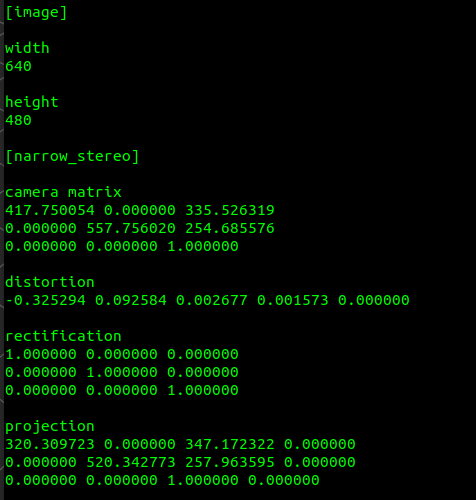
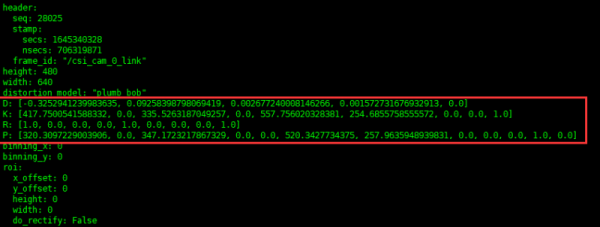
- After restarting the camera node, run the following command to check that the calibration parameters have been updated.
rostopic echo /camera_info
- [Note: At this time, the image viewed through image_view or RVIZ is still the original image of the camera, not the calibrated image. If the calibration image is displayed, it will be introduced in the OpenCV tutorial.]
→ zurück zum Hauptartikel: