ROS2 Tutorial: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
| Zeile 64: | Zeile 64: | ||
==== Service in ROS2 ==== | ==== Service in ROS2 ==== | ||
Services are a similar means of communication between nodes in ROS2 like topics. The publisher-subscriber model is used in Topics. And in services use a call-response type model. You can subscribe a node to a topic to receive specific information with ongoing updates, like you saw. However, a Service only offers data when specifically requested by a Client. | |||
The structure of the command to call a Service (send a request) is as follows: | |||
> ros2 service call <service_name> <service_type> <value> < | |||
Version vom 15. September 2022, 13:03 Uhr
ROS Tutorial
Introduction
The Robot Operating System (ROS) is a set of software libraries and tools for building robot applications. ROS2 has different packages for setting up programmes. Usually in ROS you can create packages in CPP and Python. Here we are focused in creating in packages in Python. A python package contain different files like package.xml - which contains the meta-information, setup.py - which contains the instruction set for the package to how to compile it, </package_name – which contains all the python scripts and this directory have always the same name as the package.
For creating a ROS package, it is necessary to operate in a specific workspace called ROS2 workspace. The directory on your hard drive where your ROS2 packages are stored and accessible by ROS2 is known as the ROS2 workspace. The ROS2 workspace directory is typically referred to as ros2_ws.
For create a package, you need to work specifically in ROS2^workspace. The directory on your hard drive where your ROS2 packages are stored and accessible by ROS2 is known as the ROS2 workspace. The ROS2 workspace directory is typically referred to as ros2_ws
When you need to compile a package for it make to work. The command which can be used by ROS2 to compile is the following:
> colcon build <
This command, which must be executed in the ros2 ws directory for it to function, will compile your whole src directory.
ROS2 Nodes
Each node in ROS2 should be in charge of a specific module, such as one node for managing wheel motors, another for managing a laser rangefinder, etc. Different channels are available for each node's communication with other nodes
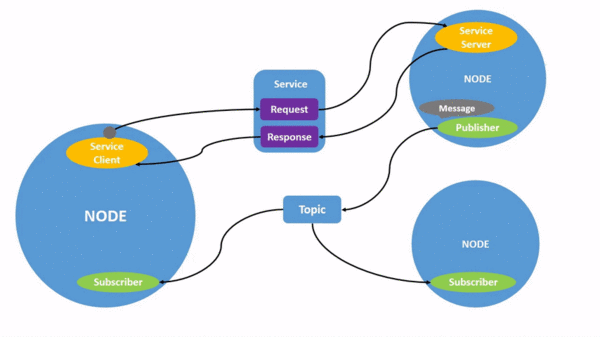
Source: here
In essence, ROS nodes are ROS programs. Use the ROS2 command to get a list of all the nodes active on a system:
> ros2 node list <
ROS client libraries enable communication between nodes created in different programming languages. Various ROS APIs require standard functionality, which is implemented by a core ROS client library (RCL). Writing client libraries for different languages is now simpler.
Basic Topic commands
There are different commands in ROS2 for various operations. The command ros2 topic list will prints a list which contains all the available Topics. The interface is divided into following groups.
Messages: This can be found as .msg files. The fields of a ROS communication are described in these straightforward text files. They can be utilized to create message source code. Services: which can be found as .srv files. A request and a response are the two pieces that make them up. Both are known as message deceleration.
Actions: Which Can be found as .action files. It contains three parts: a goal, a result, and feedback. All of these part contains a message declaration.
The .msg files and the msg/ directory of a ROS package are the two places where you can look for the descriptions and definitions for messages, respectively. The fields and constants sections make up the.msg files. The official ROS 2 documentation provide more details on this. You can read more about it here: ROS 2 documentation.
For publish a message to a topic, the ros2 topic pub command is used. The command structure is in the format as follows:
> ros2 topic pub <topic_name> <interface_name> <message> <
Topic Publisher: A topic is a place where knowledge can be read or written. A Publisher can now be described as a node that writes data into a Topic.
Custom Interface: Utilizing the interfaces that ROS2 already offers is always advised. Keep in mind that the ros2 interface list command can be used to view all ROS2 accessible interfaces. If none of them do, you can make a new one to suit your needs.
• Make a directory named msg inside your package • Make a file called name_of_your_message.msg in this directory • Change the CMakeLists.txt file • Modifypackage.xml file • Compile and source • Use in your node
Service in ROS2
Services are a similar means of communication between nodes in ROS2 like topics. The publisher-subscriber model is used in Topics. And in services use a call-response type model. You can subscribe a node to a topic to receive specific information with ongoing updates, like you saw. However, a Service only offers data when specifically requested by a Client.
The structure of the command to call a Service (send a request) is as follows:
> ros2 service call <service_name> <service_type> <value> <