Inbetriebnahme der Pixy 2.1 mit Simulink: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Zur Navigation springen
Zur Suche springen
Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
|||
| Zeile 166: | Zeile 166: | ||
= SPI laut MathWorks= | = SPI laut MathWorks= | ||
[[Datei:Simulink Pixy2 SPI.jpg|thumb|rigth|300px|Abb. 9: Einstellungen des Simulink Pixy2-Blocks SPI with | [[Datei:Simulink Pixy2 SPI.jpg|thumb|rigth|300px|Abb. 9: Einstellungen des Simulink Pixy2-Blocks SPI with CS]] | ||
[[Datei:Simulink_Pixy2_SPIwithCS.jpg|thumb|rigth|300px|Abb. 9: Einstellungen des PixyMon v2 v3.0.24]] | [[Datei:Simulink_Pixy2_SPIwithCS.jpg|thumb|rigth|300px|Abb. 9: Einstellungen des PixyMon v2 v3.0.24]] | ||
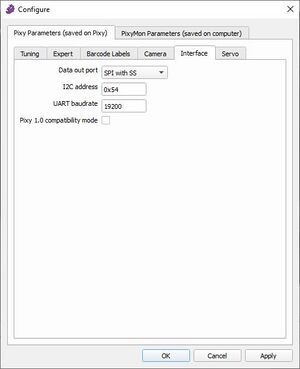
[[Datei:PixyMonSPI.jpg|thumb|rigth|300px|Abb. 9: Einstellungen des PixyMon v2 v3.0.24]] | [[Datei:PixyMonSPI.jpg|thumb|rigth|300px|Abb. 9: Einstellungen des PixyMon v2 v3.0.24]] | ||
Version vom 2. Dezember 2025, 12:09 Uhr

| Autor: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Schneider |
Software Vorbereitung
Installieren Sie folgende Software
- Simulink Coder
- Simulink Support Package for Arduino Hardware
- PixyMon v2 3.0.24
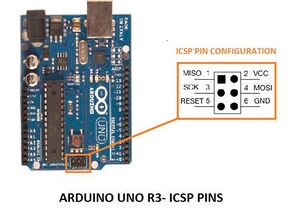
Hardware Verbindung mit Originalkabel (ISCP)
![]() Originalartikel: Hooking up Pixy to a Microcontroller
Originalartikel: Hooking up Pixy to a Microcontroller


Steckerbelegung an der Pixy 2.1 (10P)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Die Verbindung der Pixy 2 mit dem Arduino erfolgt über das mitgelieferte 6-adrige Flachbandkabel (vgl. Abb. 2 und 3).
| Pin | Pixy 2 | Arduino ICSP |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SPI MISO, UART RX, GPIO0 | SPI MISO |
| 2 | 5 V | VCC |
| 3 | SPI SCK, DAC OUT, GPIO1 | SPI SCK |
| 4 | SPI MOSI, UART TX, GPIO2 | SPI MOSI |
| 5 | I2C SCL | Reset |
| 6 | GND | GND |
| 7 | SPI SS, ADC IN, GPIO3 | |
| 8 | GND | |
| 9 | I2C SDA | |
| 10 | GND |
Problem: SPI SS (10P) ist mit Pin 5 des Arduino ICSP nicht verbunden.
| Pin | Arduino ICSP |
|---|---|
| 1 | SPI MISO |
| 2 | VCC |
| 3 | SPI SCK |
| 4 | SPI MOSI |
| 5 | Reset |
| 6 | GND |
I2C Verbindung

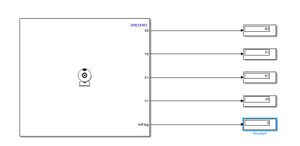
| Pin | Pixy 2 | Arduino Uno R3 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SPI MISO, UART RX, GPIO0 | |
| 2 | 5 V | VCC, 5 V |
| 3 | SPI SCK, DAC OUT, GPIO1 | |
| 4 | SPI MOSI, UART TX, GPIO2 | |
| 5 | I2C SCL | SCL |
| 6 | GND | |
| 7 | SPI SS, ADC IN, GPIO3 | |
| 8 | GND | |
| 9 | I2C SDA | SDA |
| 10 | GND | GND |
SRC
Datei:LineTrackingI2C R2025a.zip
DemoLineTrackingI2C.ino
|
#include <Pixy2I2C.h>
Pixy2I2C pixy; // Instanz erzeugen
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Serieller Monitor mit 115200 Baud gestartet...");
delay(1000);
int r = pixy.init(); // Pixy2 starten (I2C automatisch)
Serial.print("pixy.init(): ");
Serial.println(r);
Serial.println("Pixy Init ...");
delay(500);
int result = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { // 10 Verbindungsversuche
result = pixy.changeProg("line");
Serial.print("changeProg try ");
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print(": ");
Serial.println(result);
if (result >= 0) {
Serial.println("Pixy2 Line Tracking gestartet..."); // Erfolgreicher Start
delay(1000);
break;
}
}
}
void loop() {
int8_t Ergebnis_u8 = pixy.line.getMainFeatures();
if (Ergebnis_u8 <= 0) {
Serial.println("Keine Linie gefunden.");
delay(100);
return;
}
// Hauptlinie (featureType = LINE_VECTOR)
if (pixy.line.numVectors) {
Serial.print("Linie gefunden: ");
Serial.print("x0=");
Serial.print(pixy.line.vectors[0].m_x0);
Serial.print(" y0=");
Serial.print(pixy.line.vectors[0].m_y0);
Serial.print(" x1=");
Serial.print(pixy.line.vectors[0].m_x1);
Serial.print(" y1=");
Serial.println(pixy.line.vectors[0].m_y1);
}
delay(50);
}
URL: https://svn.hshl.de/svn/Informatikpraktikum_1/trunk/Arduino/ArduinoLibOrdner/Pixy2/examples/DemoLineTrackingI2C/ |
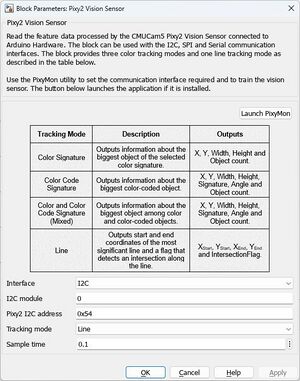
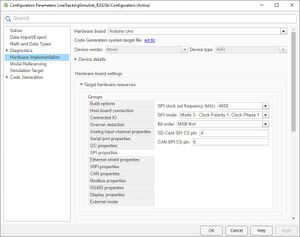
SPI laut MathWorks

| Pin | Pixy 2.1 10P | Arduino Uno R3 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SPI MISO | 12 |
| 2 | 5 V VCC | 5 V |
| 3 | SPI SCK | 13 |
| 4 | SPI MOSI | 11 |
| 6 | GND | GND |
| 7 | SPI SS | D10 |
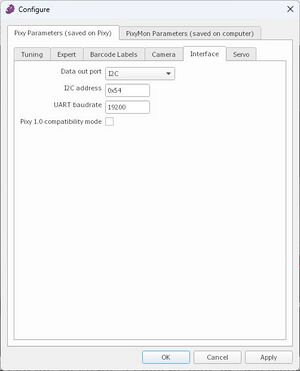
Error:
Pixy2 vision sensor supports bit order of 'MSB first' and SPI mode 3. Change the values in the 'SPI properties' of the Hardware board settings and retry.
Lösung siehe Abb.
Dokumentation
→ zurück zum Hauptartikel: Kamerasensor_Pixy_2.1