Autonomous Driving Analysis, sumarry And Conclusion: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Zur Navigation springen
Zur Suche springen
Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| Zeile 9: | Zeile 9: | ||
=== Limitations === | === Limitations === | ||
* Hardware constraints limited the maximum processing speed. | * Hardware constraints limited the maximum processing speed(without GPU Coder). | ||
* Initial data quality was poor due to randomized manual steering input. | * Initial data quality was poor due to randomized manual steering input. | ||
* Better results were obtained after switching to discrete, consistent control signals. | * Better results were obtained after switching to discrete, consistent control signals. | ||
* However, simultaneous recording, steering, and saving caused performance bottlenecks due to the Jetson Nano’s limited resources. | * However, simultaneous recording, steering, and saving caused performance bottlenecks due to the Jetson Nano’s limited resources. | ||
=== Training Results === | |||
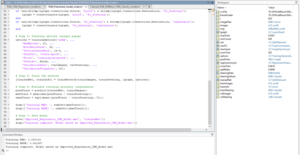
* Pretrained methods were tried but also showed poor performance. with the following parameters: | |||
[[Datei:Pretrained 50 epoch.png|mini]] | |||
[[Datei:Pretrained 50 epoch 2.png|mini]] | |||
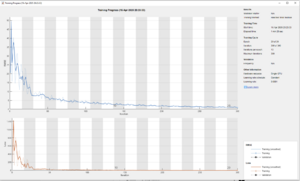
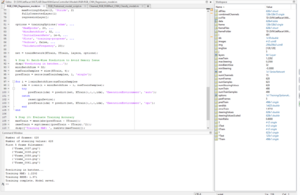
* Regression methods were tried but also showed poor performance. with the following parameters: | |||
[[Datei:regression_50_epoch2.png|mini|Fig. 9: regression_50_epoch2]] | |||
[[Datei:regression_50_epoch.png|mini|frame|Fig. 10: regression_50_epoch]] | |||
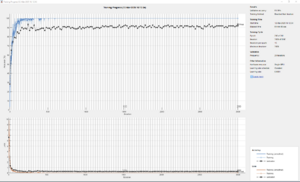
* The project switched to **classification** using **discrete steering values**. with the following parameters: | |||
[[Datei:Cleaned CNN Classify.png|mini|frame|Fig. 13: Camera setup for image recording during driving]] | |||
[[Datei:regression.png|mini]] | |||
More details of further work on Autonomous driving can be found here[]. | |||
== Summary and Outlook == | == Summary and Outlook == | ||
Version vom 12. Juni 2025, 19:38 Uhr
Autonomous Driving Neural Network Training
Experiment Analysis
- Models trained on discrete steering values showed significantly better results than regression-based approaches.
- Grayscale recordings increased model stability.
- Calibrated images helped reduce the steering error caused by lens distortion.
Limitations
- Hardware constraints limited the maximum processing speed(without GPU Coder).
- Initial data quality was poor due to randomized manual steering input.
- Better results were obtained after switching to discrete, consistent control signals.
- However, simultaneous recording, steering, and saving caused performance bottlenecks due to the Jetson Nano’s limited resources.
Training Results
- Pretrained methods were tried but also showed poor performance. with the following parameters:

- Regression methods were tried but also showed poor performance. with the following parameters:
- The project switched to **classification** using **discrete steering values**. with the following parameters:
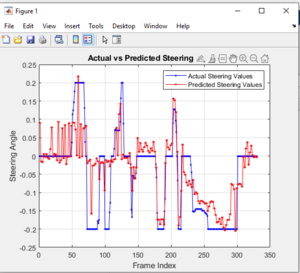
More details of further work on Autonomous driving can be found here[].
Summary and Outlook
This project demonstrated that it is possible to optimize autonomous navigation on the JetRacer using a combination of classical control algorithms and neural networks. Despite hardware limitations, stable autonomous driving behavior was achieved.
Future improvements could include:
- Expanding the dataset with more diverse environmental conditions.
- Flash working Model directly on jetson nano using gpu coder
- Use accurate gamepad and use more complex training method.
- Improving automated labeling and refining the PD controller parameters for faster driving without loss of robustness.