Use MATLAB to Train on Jetson Nano: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Zur Navigation springen
Zur Suche springen
Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| (9 dazwischenliegende Versionen desselben Benutzers werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 10: | Zeile 10: | ||
#Data preprocessing—including image resizing, augmentation, and normalization—is handled with MATLAB functions such as imageDatastore and augmentedImageDatastore. | #Data preprocessing—including image resizing, augmentation, and normalization—is handled with MATLAB functions such as imageDatastore and augmentedImageDatastore. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ Tabelle | |+ Tabelle 6: Deep Learning with MATLAB Setup | ||
|- | |- | ||
! # !! !! Description !! Pictures | ! # !! !! Description !! Pictures | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1 || Data Processing || || | | 1 || Data Processing || | ||
*Image resizing: Ensures all input images match the network’s expected dimensions. Consistent sizing improves training stability and speeds up batch processing. | |||
*Augmentation: Expands the dataset by applying random transformations—such as rotations, flips, translations, and color jitter—using imageDataAugmenter and augmentedImageDatastore. This reduces overfitting by exposing the model to varied examples without collecting new data. | |||
*Normalization: Scales pixel values to a common range (e.g., [0,1] or zero‐mean/unit‐variance). Normalized inputs ensure faster convergence and prevent numeric instability during training. | |||
|| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| 2 || Model training|| | | 2 || Model training|| Here is an important aspect of training because all training parameters, configurations and directions are ensured. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 3 || Output || || | | 3 || Output || Trained networks are exported to a .mat file, encapsulating weights, architecture, and training metadata for reuse. || | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Zeile 29: | Zeile 35: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ Tabelle | |+ Tabelle 7: GPU Coder Setup | ||
|- | |- | ||
! # !! !! Description !! Pictures | ! # !! !! Description !! Pictures | ||
|- | |- | ||
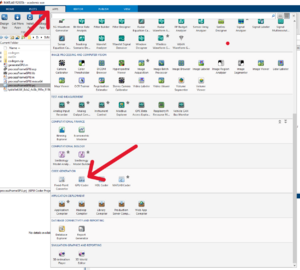
| 1 || Access GPU APP || || [[Datei:Gpu coder APP.png|mini]] | | 1 || Access GPU APP || Matlab provides built-in app to generate Cuda compatible code.|| [[Datei:Gpu coder APP.png|mini|Fig. 10: Gpu Coder APP]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
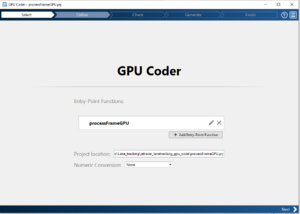
| 2 || Select Entry-Point Function|| || | | 2 || Select Entry-Point Function|| For CUDA code to be successfully generated, the MATLAB script must be a function. Hence, your script needs to be converted to a function. || | ||
[[Datei:Gpu coder function.png|mini]] | [[Datei:Gpu coder function.png|mini|Fig. 11: Gpu Coder Function]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
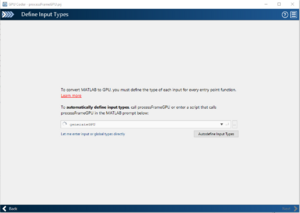
| 3 || Select Input types|| | | 3 || Select Input types|| A second file is required for the GPU Coder to Know what asre the inputs and Outputs || | ||
[[Datei:Input Types.png|mini]] | [[Datei:Input Types.png|mini|Fig. 12: Input Types]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 4 || Select Targeted GPU|| || | | 4 || Select Targeted GPU|| The CUDA code can be Generated directly on the chosen device or generated on the main pc and manually transported on the device || | ||
|- | |- | ||
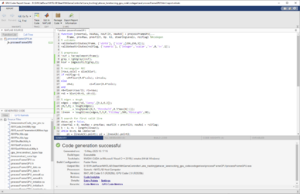
| 5 || Generate c/c++ || || | | 5 || Generate c/c++ || Check for errors and Generated folders || | ||
[[Datei:Generated Cuda Code.png|mini]] | [[Datei:Generated Cuda Code.png|mini|Fig. 13: Generated Cuda Code]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 12. Juni 2025, 22:10 Uhr
Setup
Overview
To train the AI using MATLAB, I will write a script on MATLAB and then use GPU Coder to flash the function/model on the JetRacer. So all the debugging process will be on MATLAB.
Key Concepts
- Deep Learning with MATLAB
- The fundamental of training an AI system is called deep learning. MATLAB provides a variety of helpful toolboxes, pre-trained networks, and tools to process data into useful input for an AI [1].
- The training can be stored as a model, usually in a .MAT format, which can be reused. Hence, we do not have to train a model every time we want to use it.
- Data preprocessing—including image resizing, augmentation, and normalization—is handled with MATLAB functions such as imageDatastore and augmentedImageDatastore.
| # | Description | Pictures | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data Processing |
|
|
| 2 | Model training | Here is an important aspect of training because all training parameters, configurations and directions are ensured. | |
| 3 | Output | Trained networks are exported to a .mat file, encapsulating weights, architecture, and training metadata for reuse. |
- Gpu Coder
- GPU Coder generates optimized CUDA® C++ from your MATLAB® algorithms, unlocking the parallel compute power of the Jetson GPU for real-time processing on your JetRacer and improve 40 times the performance on the jetracer [2][3].
- Helps target GPUs for automotive applications.